We are pleased to announce a new release of Automatiko - 0.16.0
Highlights
- MongoDB files addon
- Workflow instance expiration
- Persistence enhancements
- Auto discovery of persistence addons
- Use of expressions in event data mapping
MongoDB files addon
Processing files as part of workflow is a common requirement. Automatiko introduced files storage support few releases ago and that was based on
- local file system
- Amazon S3
- Google Cloud Storage
Have a look at more details about files storage in Automatiko documentation.
Workflow instance expiration
Workflow instances might be required to be kept after their completion. That might be due to legal reasons that enforce to have complete access to workflow instance
data for a given amount of time. To make this happen Automatiko has a setting of so called instance end strategy that when set to keep
will keep the completed (and aborted) workflow instances in data store. Though this entries are never removed and usually they comply with predefined retention policy.
0.16.0 comes with a feature that allows to set expiration at workflow definition level. This expiration is calculated based on the given
ISO8601 date period e.g. P30D (which stands for 30 days) and the end date of the workflow instance. This information is stored in data store and by that can be
targeted by retention policy logic that can simply clean it up based on the calculated value.
Worth noting is that when using MongoDB as persistent store for workflow instances, clean up of expired workflow instances is done automatically.
Expiration expression is set on workflow definition level via custom attribute called expiresAfter
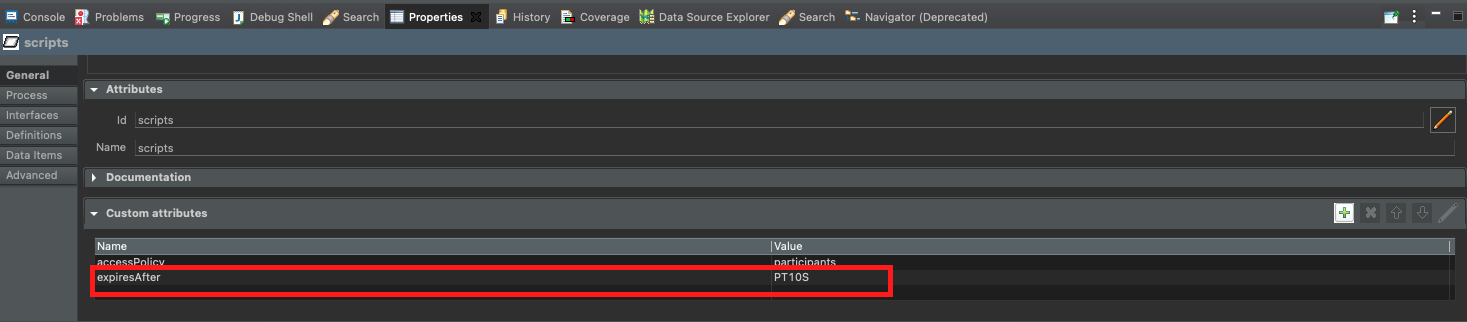 Setting expiration expression on workflow definition.
Setting expiration expression on workflow definition.
Have a look at more details about custom attributes on workflow definition in Automatiko documentation.
Persistence enhancements
All persistence addons (File system, Apache Cassandra, DynamoDB, DB, MongoDB) have been enhanced to store
- start date of the workflow instance
- end date of the workflow instance
- expiration date of the workflow instance
instance-end-strategy is set to keep. As this will
make the workflow instances to be kept in data store even after they are completed.
Important aspect here is a migration that depending on data store used might be required. See Automatiko documentation for details about migration required.
Auto discovery of persistence addons
Before 0.16.0 release, persistence addon had to be specified in two places
- added as dependency
- specified in
application.propertiesfile usingquarkus.automatiko.persistence.typeproperty
Use of expressions in event data mapping
In many cases direct workflow data object mapping to the event node is not enough. To give an example, imagine workflow definition should publish a message (or event) to the broker. The payload expected at the destination might come from multiple data objects (aka variables) managed by workflow so it is not really feasible to make it with single data mapping.
For exaclty this scenario, use of expressions is recommended. 0.16.0 comes with possibility to use expressions for event nodes (message event nodes benefit the most) to be able to perform more advanced data adjustements.
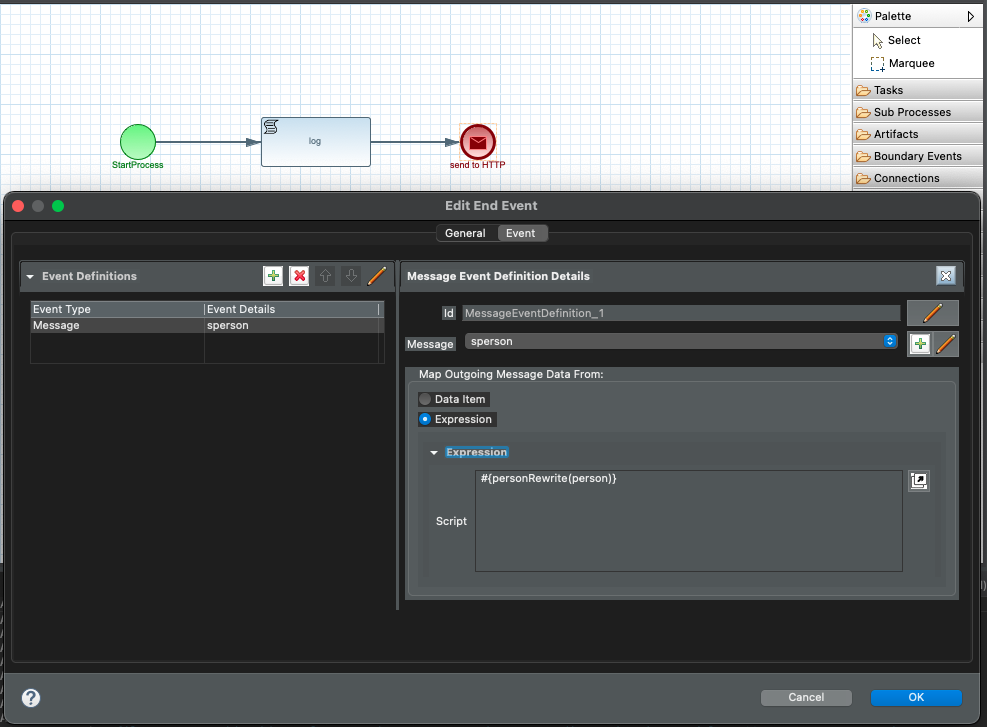 Use of expressions in message event data mapping.
Use of expressions in message event data mapping.
Note that, these expressions can directly refer to Functions that make the code really clean on both ends. Functions are
simple classes that implement io.automatiko.engine.api.Functions and expose public static methods like the example below
import io.automatiko.engine.api.Functions;
public class PersonFunctions implements Functions {
public static Person personRewrite(Person person) {
Person rewritten = new Person();
rewritten.setAge(person.getAge() + 10);
rewritten.setName(person.getName().toUpperCase());
return rewritten;
}
}
Photographs by Unsplash.